Connect to an Internal Load Balancer (ILB)
Onehouse deploys internal load balancers (ILBs) within your cloud account with the following functionality.
- Main ILB: Onehouse deploys one ILB for the project to access dashboards and monitoring within your data plane, such as the Spark UI for Job Runs.
- SQL Clusters: Each SQL Cluster deploys a new ILB to accept JDBC connections for submitting queries.
The table below describes each functionality that is exposed on an ILB, along with the specific host and port:
| Functionality | Host | Port | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apache Spark UI for SQL Clusters and Jobs | Main ILB | 80 | View the Spark UI for a Job run or SQL Cluster in your browser |
| SQL Cluster JDBC | Cluster-specific ILB | 10000 | Submit SQL queries |
| Open Engines (Trino) | Cluster-specific ILB | 8080 | Submit Trino queries and access the Trino Web UI in your browser |
| Open Engines (Apache Flink) | Cluster-specific ILB | 8080 | View the Flink UI in your browser |
| Open Engines (Ray) | Cluster-specific ILB | 8265 | Submit Ray workloads via API and access the Ray dashboard in your browser |
| Notebook Clusters | Main ILB | 8080 | Run interactive PySpark workloads on managed notebooks |
| Advanced Monitoring | Main ILB | N/A | Prometheus endpoint and Grafana metrics for the project |
ILBs are not exposed to public internet, and must be securely accessed through your VPC. This guide walks through how to access them.
If you prefer to access load balancers through public internet, Project Admins can enable that setting for the main load balancer in the project settings.
Prerequisites
To connect through your VPC from a local machine, you will need one of the following:
- VPN connected to your VPC
- Bastion host within your VPC
VPN setup
Using a virtual private network (VPN) is the simplest approach. Simply connect your local machine to the same VPC as the Onehouse project through your VPN.
Skip ahead to access the ILB.
Bastion host setup
A bastion host allows you to securely access your VPC when you don't have access through a VPN. The bastion host is reachable outside of the VPC, and can be used as a jump box to access the ILB from your local machine or other cloud tools.
Prerequisite: Bastion host
You will first need a bastion host in the same VPC as your Onehouse project. You can have Onehouse automatically create this or create it yourself.
You can use a free tier instance type for the bastion host in most cases, as the machine will simply pass network calls to the internal load balancer.
Onehouse-created bastion host
Available for AWS projects only.
In your Onehouse Terraform or CloudFormation template, you can configure Onehouse to create a bastion host in your VPC. Under the bastionHostConfig, set enabled to true.
The bastion host Onehouse creates is public internet-accessible. You can find this in EC2 (for AWS projects), in the same region as your Onehouse project. The bastion host will be named: onehouse-bastion-host-<request-id-prefix>. You can find the request ID prefix in the Onehouse console by clicking your profile in the bottom left corner.
Create it yourself
Create a new instance type in EC2 (for AWS) or GCE (for GCP), within the same VPC as your Onehouse project. Ensure the instance is accessible from the clients you want to use, such as your local machine. We recommend enabling inbound network access from all traffic.
Step 1: Get the internal load balancer host
Next, you will connect through SSH or AWS Systems Manager (SSM) and port forward the ILB to your local machine.
Get the ILB host from the Onehouse console:
- You can find the main ILB on the pages of resources that expose data through an ILB, such as:
- You can find the ILB for JDBC connnections to a SQL Cluster on the Cluster details page.
Here is an example from a Job run:
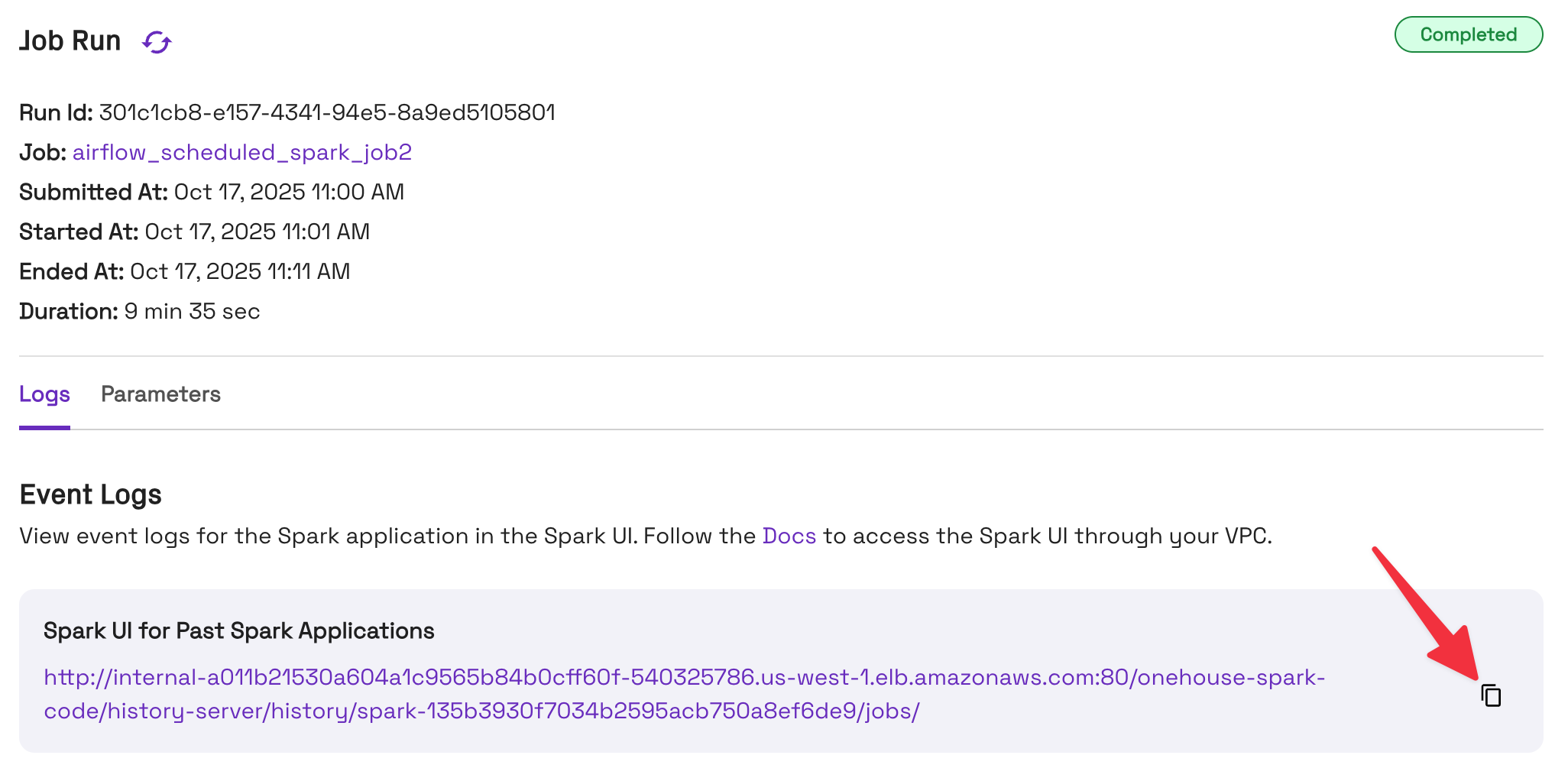
The host should look like:
internal-a011b21530a604a1c9565b84b0cff60f-540325786.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com
Copy the host to somewhere you can use it in Step 3.
Ensure that you've only copied the host. Exclude any other strings from the URL, such as "https://", the port number, and pathname after the host.
Step 2: Port forward to your local machine
In the port mappings table above, find the port number that maps to your desired functionality.
Next you will port forward the ILB to your local machine. For this step we will use an example with the following host and port:
# Host
internal-a011b21530a604a1c9565b84b0cff60f-540325786.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com
# Port
80
We will outline two potential approaches for port forward to your local machine:
- Connect with SSH through a bastion host
- Connect with AWS Systems Manager (SSM) through a bastion host (for AWS projects only)
Example: Connect with SSH through a bastion host
Connect to the bastion host through SSH and port forward to your local machine.
- Download a private key from your cloud provider to access the bastion host. Set local permissions on the key:
chmod 400 <private-key.pem> - Find the ILB host and port number you copied in the previous steps.
- Forward the target port from the ILB host to local port 10000 (or another unused port):
# Port forward template
ssh -i <private_key> -N -L 10000:<load-balancer-host>:<port-number> <user>@<bastion-host-address>
# Example filled-in
ssh -i keys/private_key.pem -N -L 10000:internal-a011b21530a604a1c9565b84b0cff60f-540325786.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com:80 ec2-user@ec2-34-55-484-192.us-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com - Keep the port forwarding open in your terminal. Move ahead to access the ILB.
Example: Connect with AWS SSM through a bastion host (AWS only)
Connect to the bastion host through AWS Systems Manager (SSM) and port forward to your local machine. This approach is only possible for Onehouse projects on AWS.
- Confirm the SSM prerequisites.
- The instance (bastion host) has the SSM Agent installed and running.
- The bastion instance IAM role includes the
AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCorepolicy. - AWS CLI is configured with credentials that allow
ssm:StartSessionandssm:StartPortForwardingSessionToRemoteHost. - Install the Session Manager plugin for the AWS CLI if you haven’t already.
- Find the ILB host and port number you copied in the previous steps.
- Start a port forwarding session to the ILB host. You can customize and run the bash script template below.
- Template script to port forward through SSM:
#!/bin/bash
# Replace with your bastion host EC2 instance ID
BASTION_INSTANCE_ID="i-012399fb76d4798ee"
# Replace with your Internal Load Balancer (ILB) DNS name
ONEHOUSE_ILB_DNS="internal-a011b21530a604a1c9565b84b0cff60f-540325786.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com"
# Replace with the port you are connecting to
TARGET_PORT=80
# Keep 10000 or change to another open local port
LOCAL_PORT=10000
# Optionally add region, if your SSM setup requires it
aws ssm start-session \
--target "$BASTION_INSTANCE_ID" \
--document-name AWS-StartPortForwardingSessionToRemoteHost \
--parameters "{\"host\":[\"$ONEHOUSE_ILB_DNS\"],\"portNumber\":[\"$TARGET_PORT\"],\"localPortNumber\":[\"$LOCAL_PORT\"]}" - Save the script with your preferred filename (e.g.,
connect-ilb.sh), then run it:./connect-ilb.sh
- Template script to port forward through SSM:
- Keep the port forwarding open in your terminal. Move ahead to access the ILB.
Access the internal load balancer
You should now be connected through your VPC and able to access the ILB. You can access the ILB based on your chosen approach.
- Access via VPN: Use the full ILB URL.
# Example
http://internal-a011b21530a604a1c9565b84b0cff60f-540325786.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com:80/onehouse-spark-code/history-server/history/spark-135b3930f7034b2595acb750a8ef6de9/jobs/ - Access via bastion host: Replace the host in the ILB URL with the
localhostforwarded port you configured.# Example
http://localhost:10000/onehouse-spark-code/history-server/history/spark-135b3930f7034b2595acb750a8ef6de9/jobs/
Finally, follow the steps from the feature-specific documentation to to access event logs, submit SQL queries, and more. Below are some examples: