Connect to a SQL Cluster via Bastion Host
By default, SQL Clusters require that you connect from within your VPC. You can achieve this with a VPN or by connecting through a bastion host.
This guide provides a tutorial for creating a bastion host and using it to connect to a SQL Cluster.
Create a Bastion Host
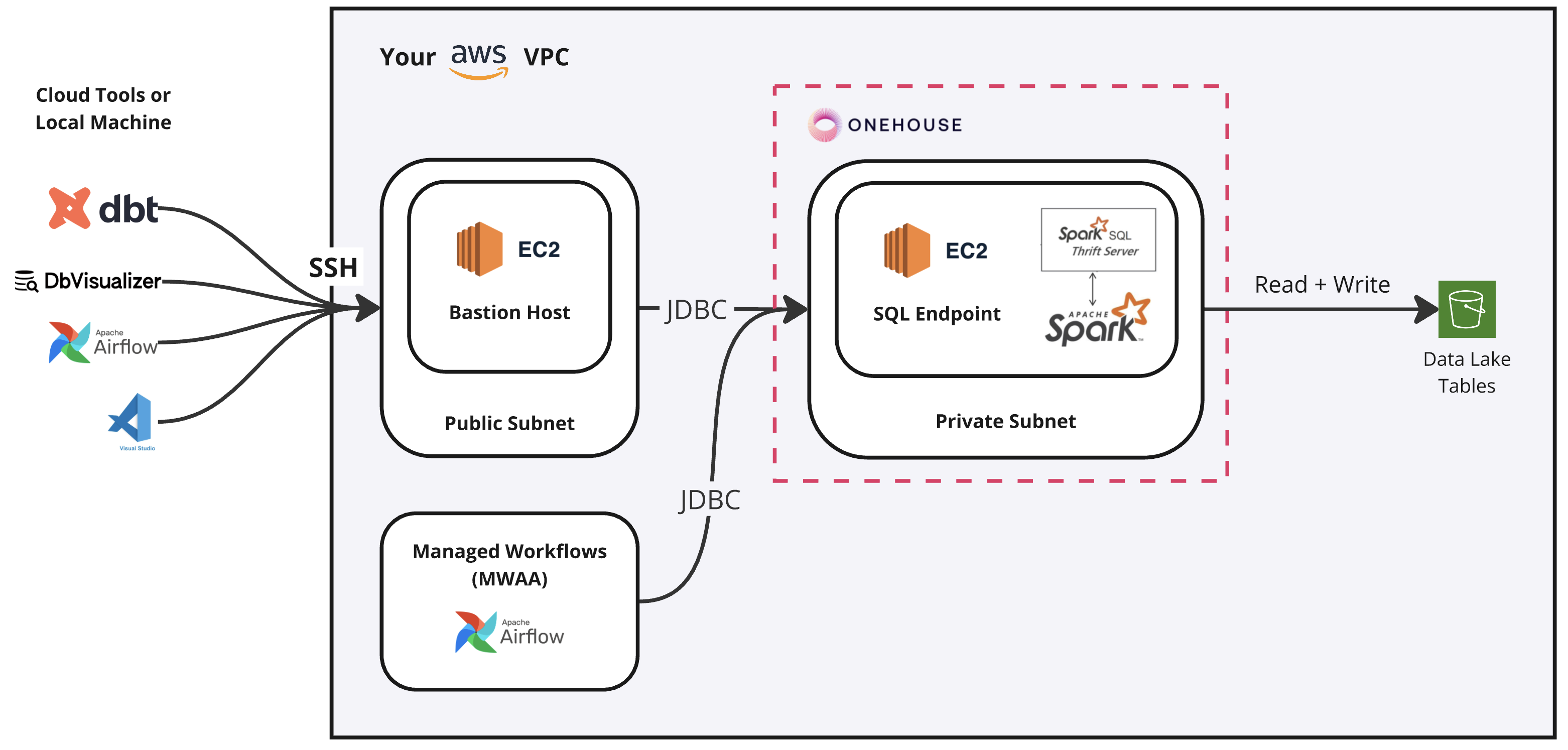
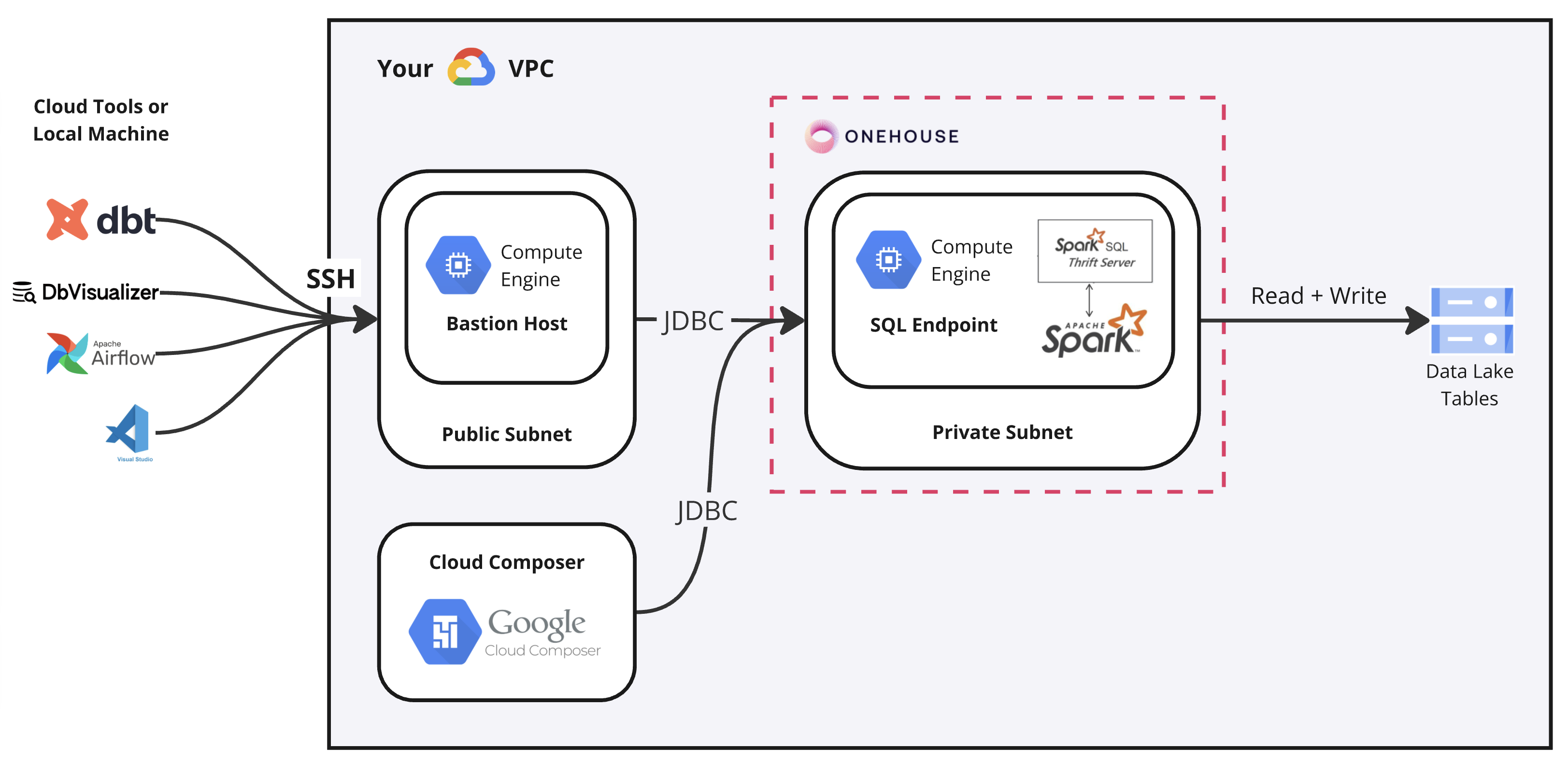
A simple and secure way to access the SQL Cluster is to create a new AWS EC2 or Google Compute Engine instance within your VPC to serve as a bastion host. The bastion host is reachable outside of the VPC through SSH, and can be used a jump box to access the SQL Cluster from cloud tools or your local machine.
You can use a free tier instance type for the bastion host in most cases, as the machine will simply submit queries to the SQL Cluster for execution.
A bastion host is not required, but can help streamline development. For example, you can use the bastion host to perform queries with SQL clients such as DbVisualizer or beeline on your local machine. The examples below show how the bastion host can route queries from cloud tools or local machines to the SQL Cluster, in addition to orchestration running within the VPC with MWAA (AWS) and Cloud Composer (GCP).
AWS Architecture Example
GCP Architecture Example
Connect to the SQL Cluster Endpoint through the Bastion Host
You can connect to the SQL Cluster endpoint using the bastion host through a local terminal by running the following command:
ssh -N <user>@<bastion-host-address> -L 10000:<sql-cluster-endpoint>:10000
Here is an example:
ssh -N ec2-user@ec2-34-55-484-192.us-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com -L 10000:internal-a49857b390fb38479c49fd19405cd30-1293045812.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com:10000
After connecting to the bastion host, keep it running in your terminal. Now you can connect to your endpoint with any tool using localhost:10000.
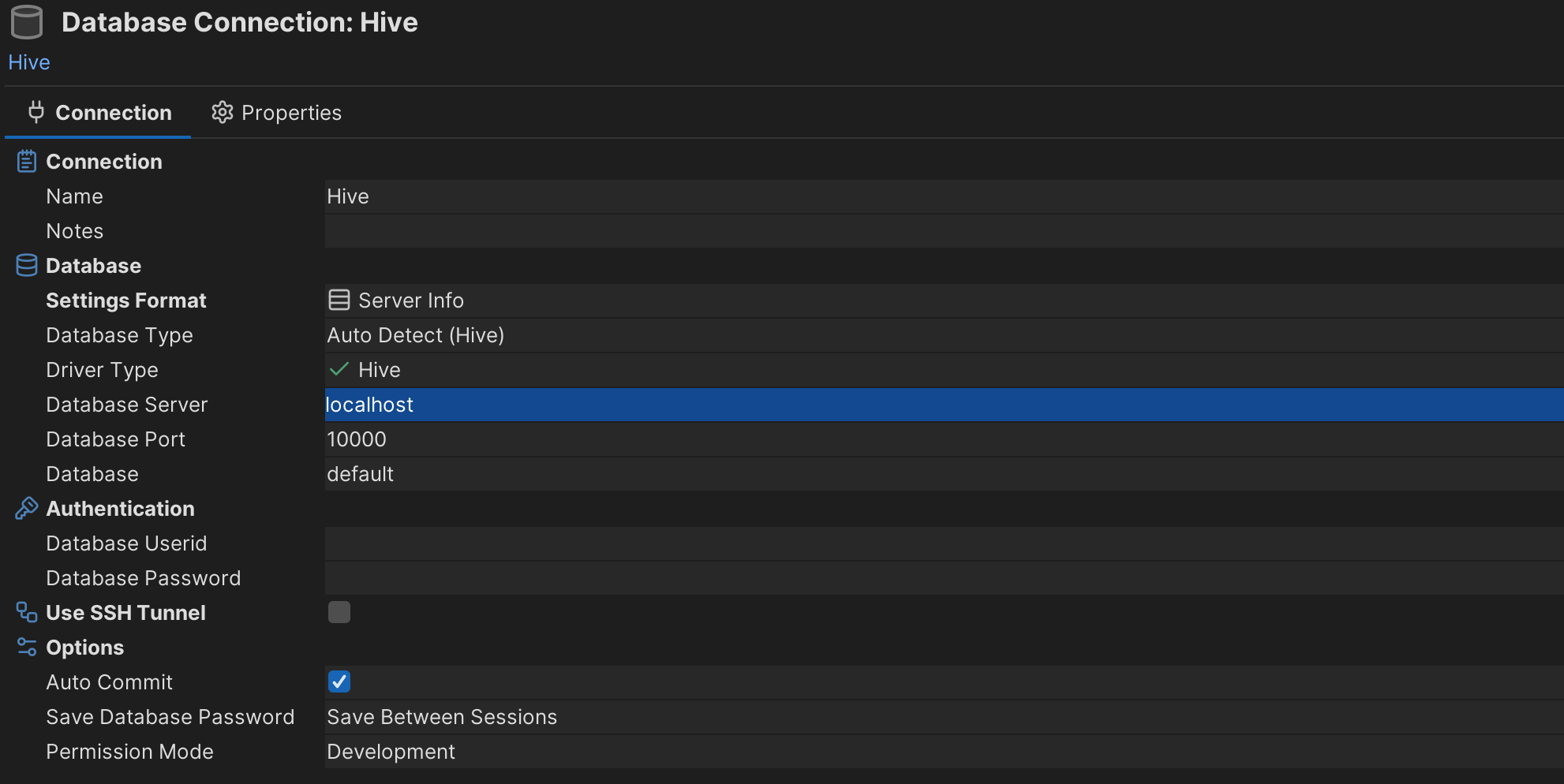
Example with DbVisualizer:
Test Connection with beeline
beeline is a client for running Spark SQL queries on a Thrift Server via the command line with a JDBC connection.
- SSH into your bastion host (skip this if you are already connected to the bastion host in a local terminal)
- Download the beeline client included in the Spark 3.5.2 (with Hadoop3) distribution
- Find your SQL Cluster endpoint on the Cluster details page in the Onehouse console
- Use the beeline CLI for interactive queries with the following command (make sure to specify a database):
Here are some sample commands with the beeline CLI:
$ beeline -u jdbc:hive2://<SQL-CLUSTER-ENDPOINT>:10000/<DATABASE-NAME>- Find an existing table in the Onehouse console or with SQL:
$ show databases;
$ use <database>;
$ show tables; - Query the existing table with beeline
$ select * from <database>.<table>;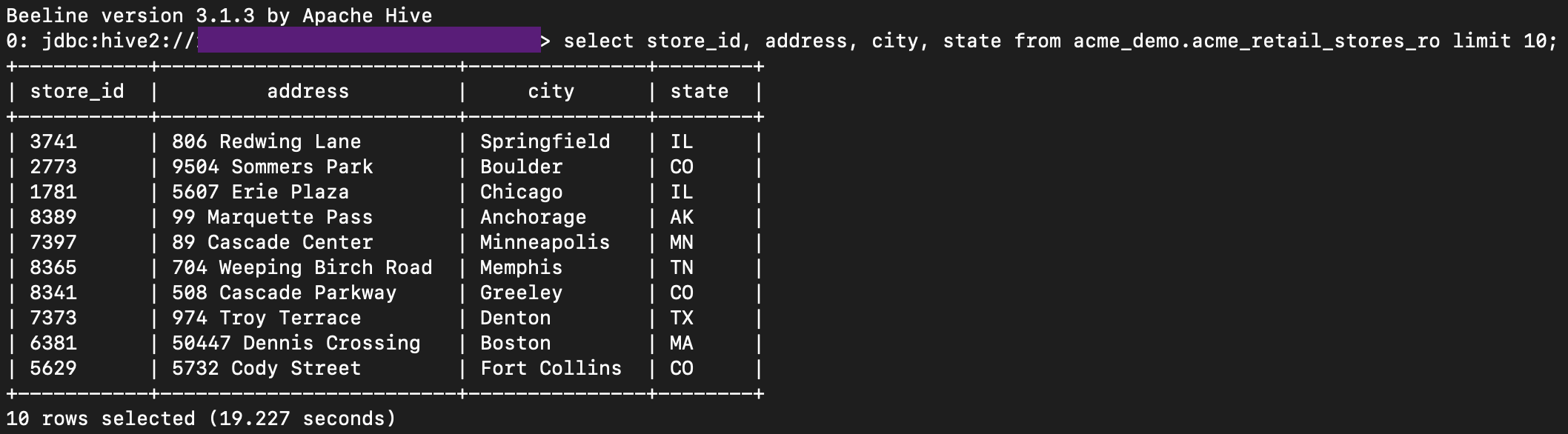
- Find an existing table in the Onehouse console or with SQL:
- Use beeline to execute queries from a file on your bastion host using the following command (make sure to specify a database):
Note: For best performance, run beeline in interactive mode (step 4) to avoid new session startup time with each query.
$ beeline -u jdbc:hive2://<SQL-CLUSTER-ENDPOINT>:10000/<DATABASE-NAME> -f <SQL-FILEPATH-TO-EXECUTE>
Example with Visual Studio Code
You can connect Visual Studio Code (VS Code) to the SQL Cluster from within your VPC. With VS Code, you can create and edit files in the VPC (eg. SQL queries or dbt models) and run commands via command line.
- Connect VS Code to your bastion host using SSH (see tutorial). You will need to install the Remote SSH VS Code plugin from Microsoft and create a configuration file with the credentials for your bastion host.
- After VS Code is connected to your bastion host, you will be able to connect to the SQL Cluster from within the VPC to run read/write queries (eg. with beeline) and dbt models.