Connect dbt Cloud
This guide outlines the steps to connect dbt Cloud to a Onehouse SQL Cluster and run the Jaffle Shop example project.
Requirements
- For dbt Cloud, ensure your Onehouse SQL endpoint is accessible via external DNS/IP, whitelisting dbt Cloud IPs.
- For dbt Core, you can SSH tunnel into the VPC to access the endpoint, without opening up ports.
What works
- All dbt features like
dbt clean,dbt compile,dbt debug,dbt seed, anddbt run. - dbt materialized type of "table" and "incrementals" .
- Apache Hudi table types of Merge on Read (MoR) and Copy on Write (CoW). It is recommended to use MoR for mutable workloads.
Limitations
- dbt materialized type cannot be "view".
dbt seedhas row / record limits.dbt seedonly supports CoW tables.
dbt connection
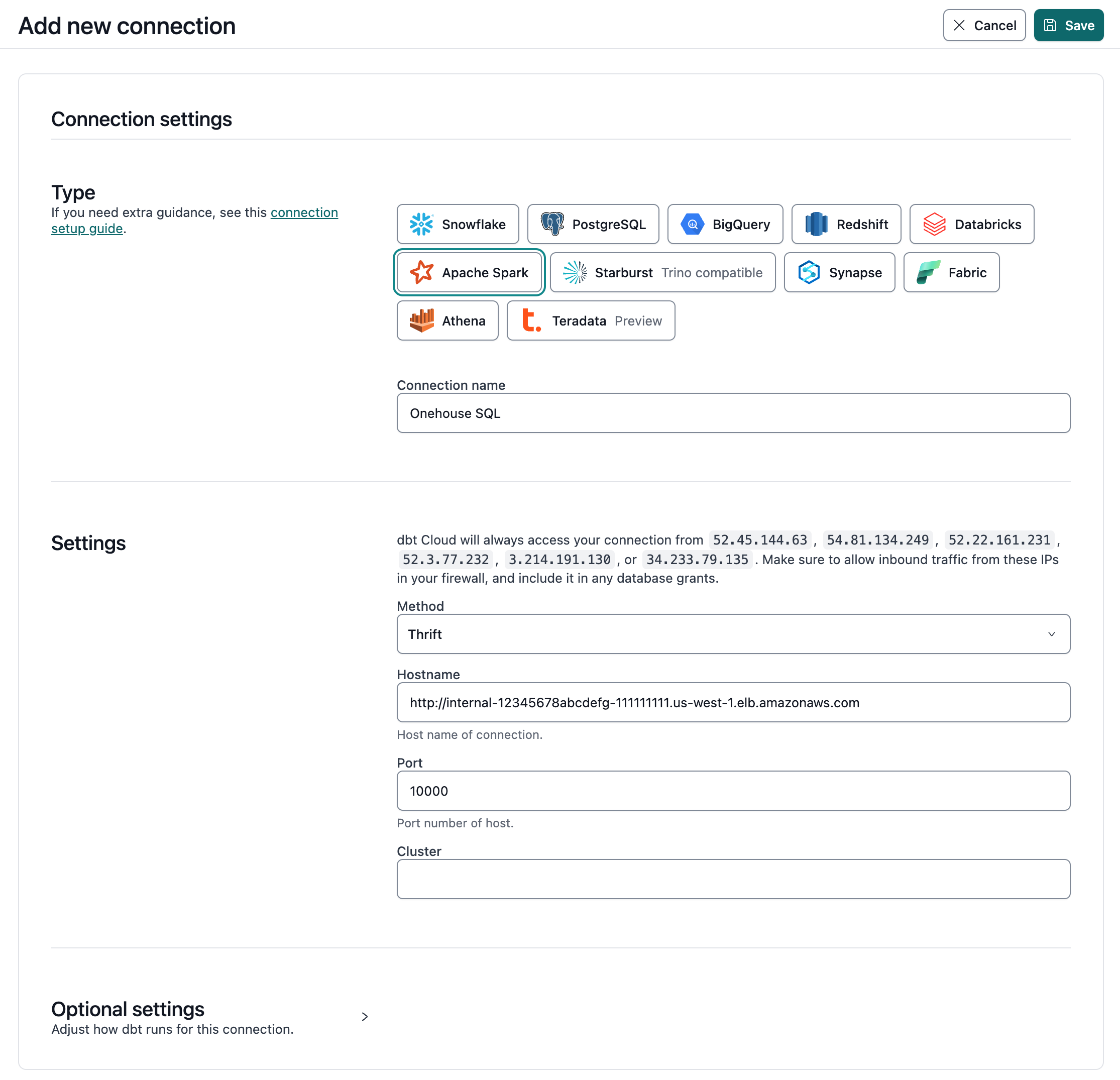
Fill in the following fields when creating an Apache Spark warehouse connection using the Thrift connection method:
| Field | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Method | The method for connecting to Spark | Thrift |
| Hostname | The hostname of your Onehouse SQL Cluster endpoint | yourProject.sparkHost.com |
| Port | The port to connect to Spark on | 10000 |
| Cluster | Onehouse does not use this field | |
| Connection Timeout | Number of seconds after which to timeout a connection | 10 |
| Connection Retries | Number of times to attempt connecting to cluster before failing | 0 |
| Organization | Onehouse does not use this field | |
| User | Optional. Not enabled by default. | dbt_cloud_user |
| Auth | Optional, supply if using Kerberos. Not enabled by default. | KERBEROS |
| Kerberos Service Name | Optional, supply if using Kerberos. Not enabled by default. | hive |
dbt project
When using dbt, ensure you add necessary configurations to dbt_project.yml for the dbt connector to write data correctly.
| Field | Description | Required | Default | Recommended |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| materialized | Type of table materialization | Yes | table | |
| file_format | Open table format to write | Yes | hudi | |
| location_root | Location of the database in DFS | Yes | ||
| hoodie.table.type | Merge on Read or Copy on Write | No | cow | mor |
dbt_project.yml template
+materialized: table | incremental
+file_format: hudi
+location_root: s3://lakehouse/demolake/dbt_ecomm/
+tblproperties:
hoodie.table.type: mor | cow
An dbt_project.yml example if using jaffle shop would be
models:
jaffle_shop:
+file_format: hudi
+location_root: s3://lakehouse/demolake/dbt_ecomm/
+tblproperties:
hoodie.table.type: mor
staging:
+materialized: incremental
marts:
+materialized: table
Quickstart
Steps
-
Download Jaffle Shop at https://github.com/dbt-labs/jaffle-shop
-
Create 2 Onehouse databases either in the UI or API
- Create a "raw" database. This is hard coded in the dbt project. If you want to change it, modify dbt_project.yml and models/staging/__sources.yml.
- Create a "dbt_awong" (this is set in dbt environment).
-
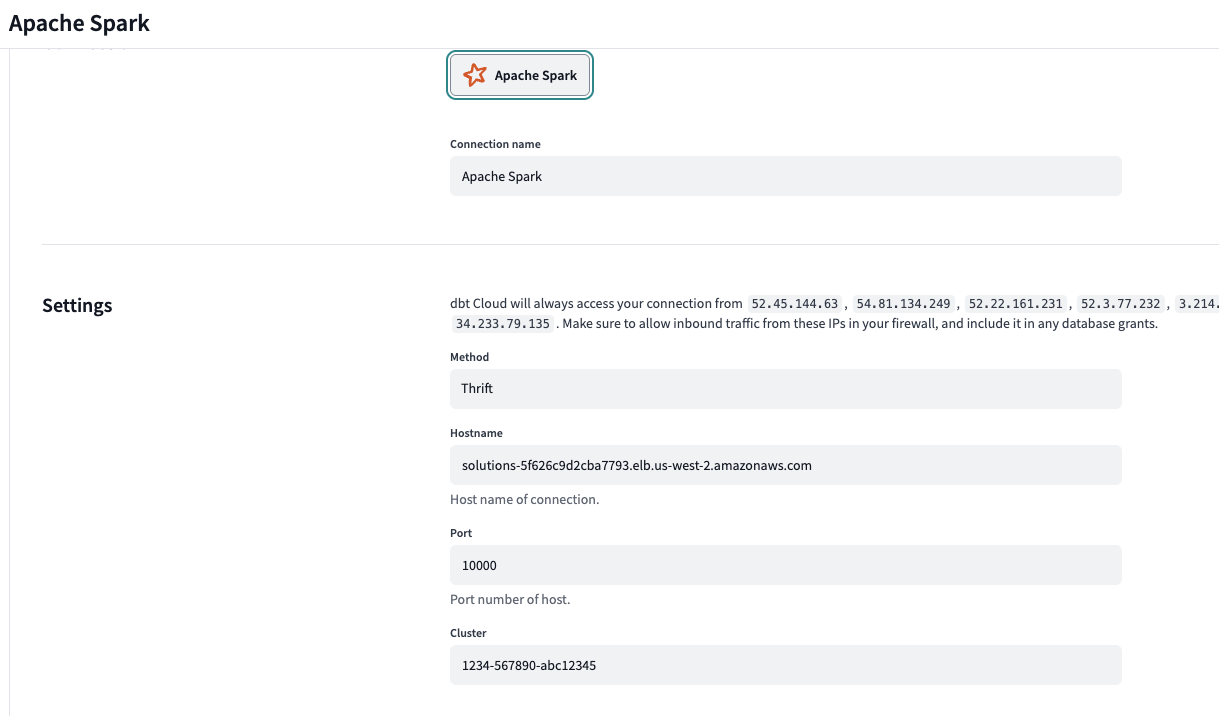
Create a DBT cloud connection of type Apache Spark. The cluster field can have a dummy entry.
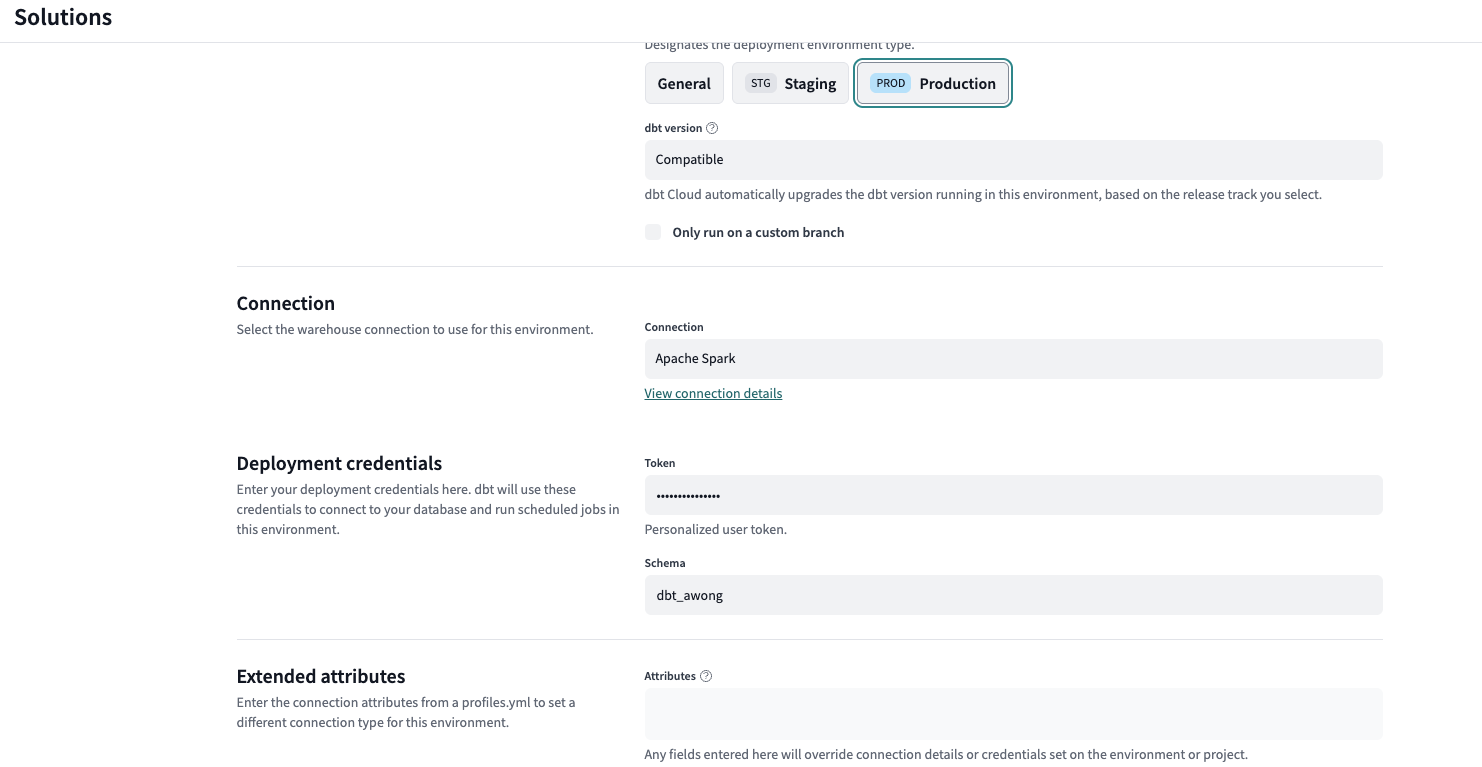
- Create a DBT environment. We will set the connection to the DBT Environemtn of Apache Spark. The token will automatically be filled in if left blank. Schema is your choice and in this example we picked "dbt_awong".
- Modify the code to support Apache Hudi. Add the file_format and location_root variables to your dbt_project.yml
seeds:
jaffle_shop:
+schema: raw
+file_format: hudi
+location_root: s3://lakehouse-albert-us-west-2/demolake/raw
+tblproperties:
hoodie.table.type: mor
models:
jaffle_shop:
+file_format: hudi
+location_root: s3://lakehouse-albert-us-west-2/demolake/dbt_awong
+tblproperties:
hoodie.table.type: mor
staging:
+materialized: table
marts:
+materialized: table
- Modify the macros/cents_to_dollars.sql to use Apache Spark SQL syntax.
{% macro spark__cents_to_dollars(column_name) -%}
CAST({{ column_name }} / 100 AS numeric(16, 2))
{%- endmacro %}
- Due to dbt Spark limitations, reduce the size of the raw_orders.csv to 7500 rows.
- Run
dbt seedanddbt runto deploy the tables and use your favorite query engine to view the data.