Apache Hudi Quickstart with SQL
Below is a subset of the Apache Hudi Spark SQL quickstart documentation, which will help you get up and running with SQL Clusters. Also see the Apache Hudi docs for full quickstarts on SQL DDL and SQL DML.
When creating Hudi tables with a SQL Cluster, you may exclude the LOCATION parameter to create the table under the storage path of the table's database.
Create Table
Use the standard CREATE TABLE syntax to create tables, with support for partitioning and passing table properties.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
[(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name, ...)]
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
[STORED AS file_format]
[LOCATION path]
[TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)]
[AS select_statement];
Example:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS hudi_table_keyed (
id INT,
name STRING,
price DOUBLE,
ts BIGINT
)
USING hudi
TBLPROPERTIES (
type = 'mor',
primaryKey = 'id',
preCombineField = 'ts'
);
Create Table As Select (CTAS)
Use CTAS (Create Table As Select) for initial loads into the table. To ensure this is done efficiently, CTAS uses bulk insert as the write operation.
Example:
# create managed parquet table
CREATE TABLE parquet_table
USING parquet
# CTAS by loading data into Hudi table
CREATE TABLE hudi_table_ctas
USING hudi
TBLPROPERTIES (
type = 'mor',
primaryKey = 'id',
preCombineField = 'ts'
)
PARTITIONED BY (dt)
AS SELECT * FROM parquet_table;
In the examples above, primaryKey specifies the Record Key for the Hudi table.
Insert Into
Use the INSERT INTO statement to add data to a table.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO <table>
SELECT <columns> FROM <source>;
Examples:
-- Insert into a Merge on Read (MoR) Hudi table
INSERT INTO hudi_mor_tbl SELECT 1, 'a1', 20, 1000;
-- Insert into a Merge on Read (MoR) Hudi table with static partition
INSERT INTO hudi_mor_pt_tbl PARTITION(dt = '2021-12-09', hh = '11') SELECT 2, 'a2', 20, 1000;
-- Insert into a Merge on Read (MOR) Hudi table with dynamic partition
INSERT INTO hudi_mor_pt_tbl PARTITION(dt, hh)
SELECT 1 AS id, 'a1' AS name, 20 AS ts, '2021-12-09' AS dt, '10' AS hh, 1000 AS timestamp;
Insert Overwrite
Use the INSERT OVERWRITE statement to replace existing data in a table. All existing partitions that are affected by the INSERT OVERWRITE statement will replaced with the source data.
Syntax:
INSERT OVERWRITE <table>
SELECT <columns> FROM <source>;
Examples:
-- Overwrite non-partitioned Hudi table
INSERT OVERWRITE hudi_mor_tbl SELECT 99, 'a99', 20.0, 900;
-- Overwrite partitioned Hudi table with dynamic partition
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE hudi_mor_pt_tbl SELECT 10, 'a10', 1100, '2021-12-09', '10', 2000;
-- Overwrite partitioned Hudi table with static partition
INSERT OVERWRITE hudi_mor_pt_tbl PARTITION(dt = '2021-12-09', hh='12') SELECT 13, 'a13', 1100, 2000;
Update
Use the UPDATE statement to modify existing data in a table directly. Note that the UPDATE operation requires you to specify a preCombineField.
Syntax:
UPDATE tableIdentifier SET column = EXPRESSION(,column = EXPRESSION) [ WHERE boolExpression]
Examples:
-- Update data in a Hudi table
UPDATE hudi_tbl SET price = price * 2, ts = 1111 WHERE id = 1;
-- Update data in a partitioned Hudi table
UPDATE hudi_pt_tbl SET name = 'a1_1', ts = 1001 WHERE id = 1;
-- Update using non record key field
UPDATE hudi_pt_tbl SET ts = 1001 where name = 'a1';
Merge Into
Use MERGE INTO to perform more complex updates and merges against source data. The MERGE INTO statement is similar to the UPDATE statement, but it allows you to specify different actions for matched and unmatched records.
Syntax:
MERGE INTO tableIdentifier AS target_alias
USING (sub_query | tableIdentifier) AS source_alias
ON <merge_condition>
[ WHEN MATCHED [ AND <condition> ] THEN <matched_action> ]
[ WHEN NOT MATCHED [ AND <condition> ] THEN <not_matched_action> ]
<merge_condition> =A equal bool condition
<matched_action> =
DELETE |
UPDATE SET * |
UPDATE SET column1 = expression1 [, column2 = expression2 ...]
<not_matched_action> =
INSERT * |
INSERT (column1 [, column2 ...]) VALUES (value1 [, value2 ...])
WHEN NOT MATCHED clauses specify the action to perform if the values do not match.
There are two kinds of INSERT clauses:
INSERT *clauses require that the source table has the same columns as those in the target table.INSERT (column1 [, column2 ...]) VALUES (value1 [, value2 ...])clauses do not require to specify all the columns of the target table. For unspecified target columns, insert theNULLvalue.
Examples:
-- Source table using Hudi for testing merging into a non-partitioned MOR table
CREATE TABLE merge_source (id INT, name STRING, price DOUBLE, ts BIGINT)
USING hudi
TBLPROPERTIES (primaryKey = 'id', preCombineField = 'ts');
-- Insert test data into source table
INSERT INTO merge_source VALUES (1, "old_a1", 22.22, 900), (2, "new_a2", 33.33, 2000), (3, "new_a3", 44.44, 2000);
-- Merge into Hudi Merge-On-Read non-partitioned table with explicit column mapping
MERGE INTO hudi_mor_tbl AS target
USING merge_source AS source ON target.id = source.id
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET *
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT *;
-- Source table using Parquet for testing merging into a partitioned table
CREATE TABLE merge_source2 (id INT, name STRING, flag STRING, dt STRING, hh STRING)
USING parquet
-- Insert test data into source table
INSERT INTO merge_source2 VALUES (1, "new_a1", 'update', '2021-12-09', '10'), (2, "new_a2", 'delete', '2021-12-09', '11'), (3, "new_a3", 'insert', '2021-12-09', '12');
-- Merge into Hudi Merge-On-Read partitioned table
MERGE INTO hudi_mor_pt_tbl AS target
USING (SELECT id, name, '1000' AS ts, flag, dt, hh FROM merge_source2) AS source
ON target.id = source.id
WHEN MATCHED AND flag != 'delete' THEN UPDATE SET id = source.id, name = source.name, ts = source.ts, dt = source.dt, hh = source.hh
WHEN MATCHED AND flag = 'delete' THEN DELETE
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (id, name, ts, dt, hh) VALUES(source.id, source.name, source.ts, source.dt, source.hh);
For a Hudi table with user configured primary keys, the join condition in Merge Into is expected to contain the primary keys of the table.
For a Table where Hudi auto generates primary keys, the join condition in MIT can be on any arbitrary data columns.
Delete From
Use DELETE FROM to remove data from a table.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM tableIdentifier [ WHERE boolExpression ]
Examples:
-- Delete data from a Hudi table
DELETE FROM hudi_mor_nonpcf_tbl WHERE uuid = 1;
-- Delete data from a MOR Hudi table based on a condition
DELETE FROM hudi_mor_tbl WHERE id % 2 = 0;
-- Delete data using a non record key field
DELETE FROM hudi_mor_pt_tbl WHERE name = 'a1';
Show and Drop Partitions
Use SHOW PARTITIONS to show partitions in a table and ALTER TABLE _ DROP PARTITION to drop a partition from the table.
Syntax:
-- Show partitions
SHOW PARTITIONS tableIdentifier;
-- Drop partition
ALTER TABLE tableIdentifier DROP PARTITION ( partition_col_name = partition_col_val [ , ... ] );
Examples:
--Show partitions
SHOW PARTITIONS hudi_table;
--Drop partition
ALTER TABLE hudi_table DROP PARTITION (dt='2021-12-09', hh='10');
Incremental Queries
Incremental queries allow you to retrieve a set of records that changed between a start and end commit time, providing you with the "latest state" for the record as of the end commit time.
Syntax:
-- syntax
hudi_table_changes(table or path, queryType, beginTime [, endTime]);
-- table or path: table identifier, example: db.tableName, tableName,
-- or path for of your table, example: path/to/hudiTable
-- in this case table does not need to exist in the metastore,
-- queryType: incremental query mode, example: latest_state, cdc
-- (for cdc query, first enable cdc for your table by setting cdc.enabled=true),
-- beginTime: instantTime to begin query from, example: earliest, 202305150000,
-- endTime: optional instantTime to end query at, example: 202305160000,
Examples:
-- start from earliest available commit, end at latest available commit.
SELECT * FROM hudi_table_changes('db.table', 'latest_state', 'earliest');
-- start from earliest, end at 202305160000.
SELECT * FROM hudi_table_changes('table', 'latest_state', 'earliest', '202305160000');
-- start from 202305150000, end at 202305160000.
SELECT * FROM hudi_table_changes('table', 'latest_state', '202305150000', '202305160000');
User-Defined Functions (UDFs)
Java and Scala UDFs are currently supported. Use the CREATE FUNCTION command to create a function that can execute code from a JAR.
First, upload your code as a JAR file in the Onehouse console under Settings > Integrations > Manage JARs. When you upload the JAR, Onehouse will add it to your S3/GCS bucket under the path:
onehouse-customer-bucket-<REQUEST_ID_PREFIX>/hudi_configs/custom_jar/jar_name.jar
Next, restart your SQL Cluster(s) to pick up the new JARs. You can do this from the Cluster page in the Onehouse console. Note that triggering a Cluster restart will kill all in-progress queries.
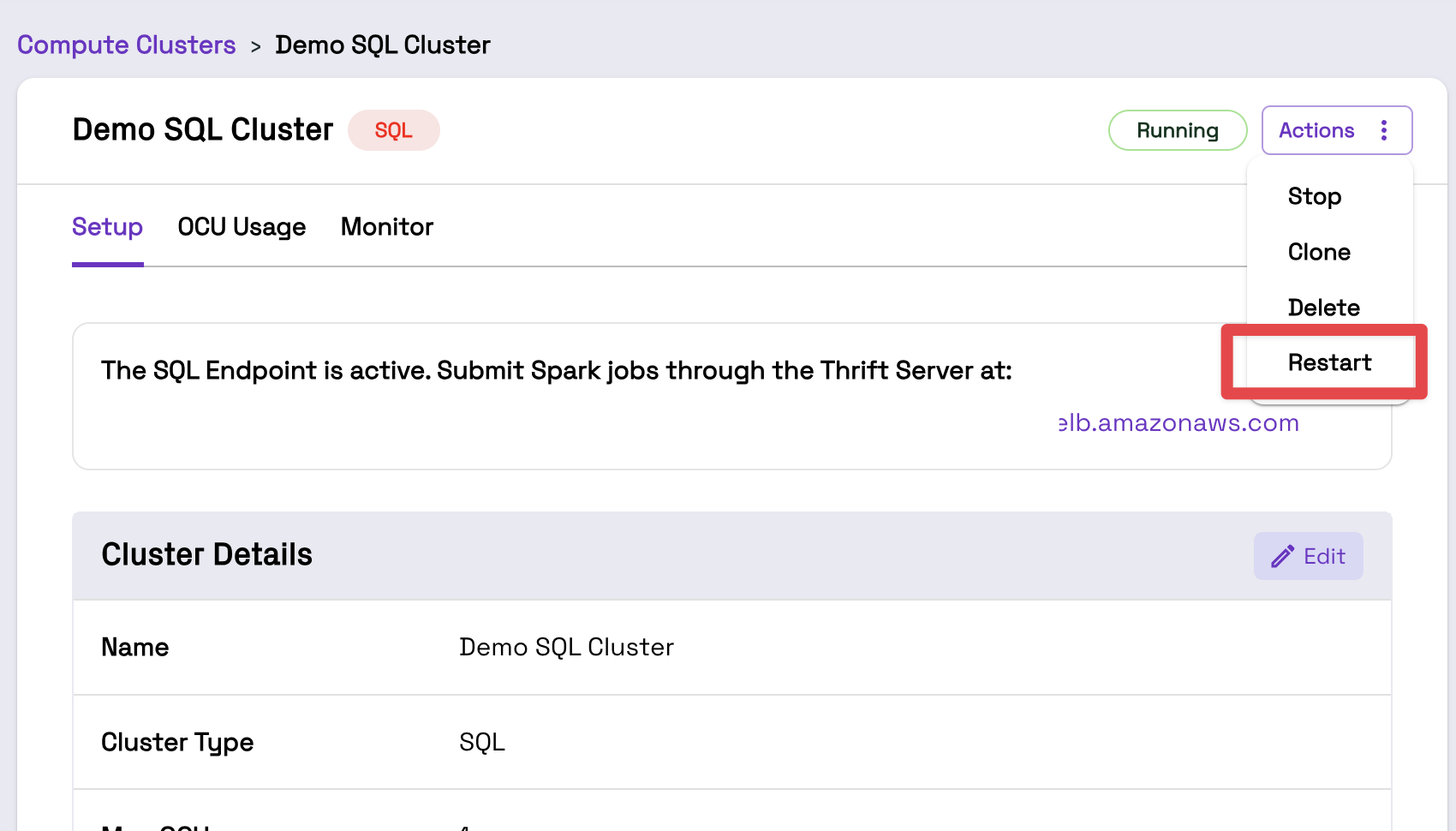
Now, you create a UDF referencing the JAR files in your SQL queries.
Syntax:
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] [ TEMPORARY ] FUNCTION [ IF NOT EXISTS ]
function_name AS class_name [ resource_locations ]
Example:
--Create the UDF by referenceing your JAR file
CREATE FUNCTION simple_udf AS 'SimpleUdf'
USING JAR 's3a://onehouse-customer-bucket-12345/hudi_configs/custom_jar/SimpleUdf.jar';
--Invoke the UDF
SELECT simple_udf(c1) AS function_return_value FROM test;
Drop Table (and Purge)
Use DROP TABLE or DROP TABLE IF EXISTS to drop the table from all metastores (including the Onehouse console). This will NOT delete the table in storage.
Examples:
DROP TABLE employeetable;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employeetable;
Use DROP TABLE PURGE to drop the table from all metastores AND delete the table in storage.
Example:
DROP TABLE employeetable PURGE;