Trino
Trino is great for performing analytical SQL queries on your Onehouse tables. Onehouse SQL is built on Apache Spark and is optimized for data pipelines (ie. write workloads), while Trino is optimized for data exploration and analysis (ie. read workloads).
Trino Clusters run on early access to an upcoming version of Trino with additional capabilities for Apache Hudi tables, including data skipping with column stats and record index and partition pruning.
Connect to a Catalog
Trino Clusters connect to an external Glue or DataProc catalog that provides the schemas of the tables you can read from. You will select this catalog during Cluster creation.
Submit and Monitor Queries
Each Trino Cluster exposes a Trino Coordinator endpoint on port 8080. You can connect to this endpoint via JDBC to submit queries with your SQL client of choice. We recommend DBeaver or DbVisualizer. You can monitor queries in the Trino Web UI at the same endpoint.
Set Trino Properties
The default Trino properties should work well for most queries, but Onehouse provides flexibility if you need to adjust your Trino properties. You can set any Trino property with Trino's SET command; view the Trino properties reference here.
Example: Connect to Trino
First, navigate to your Trino Open Engines Cluster in the Onehouse console. Copy the Trino coordinator endpoint url.
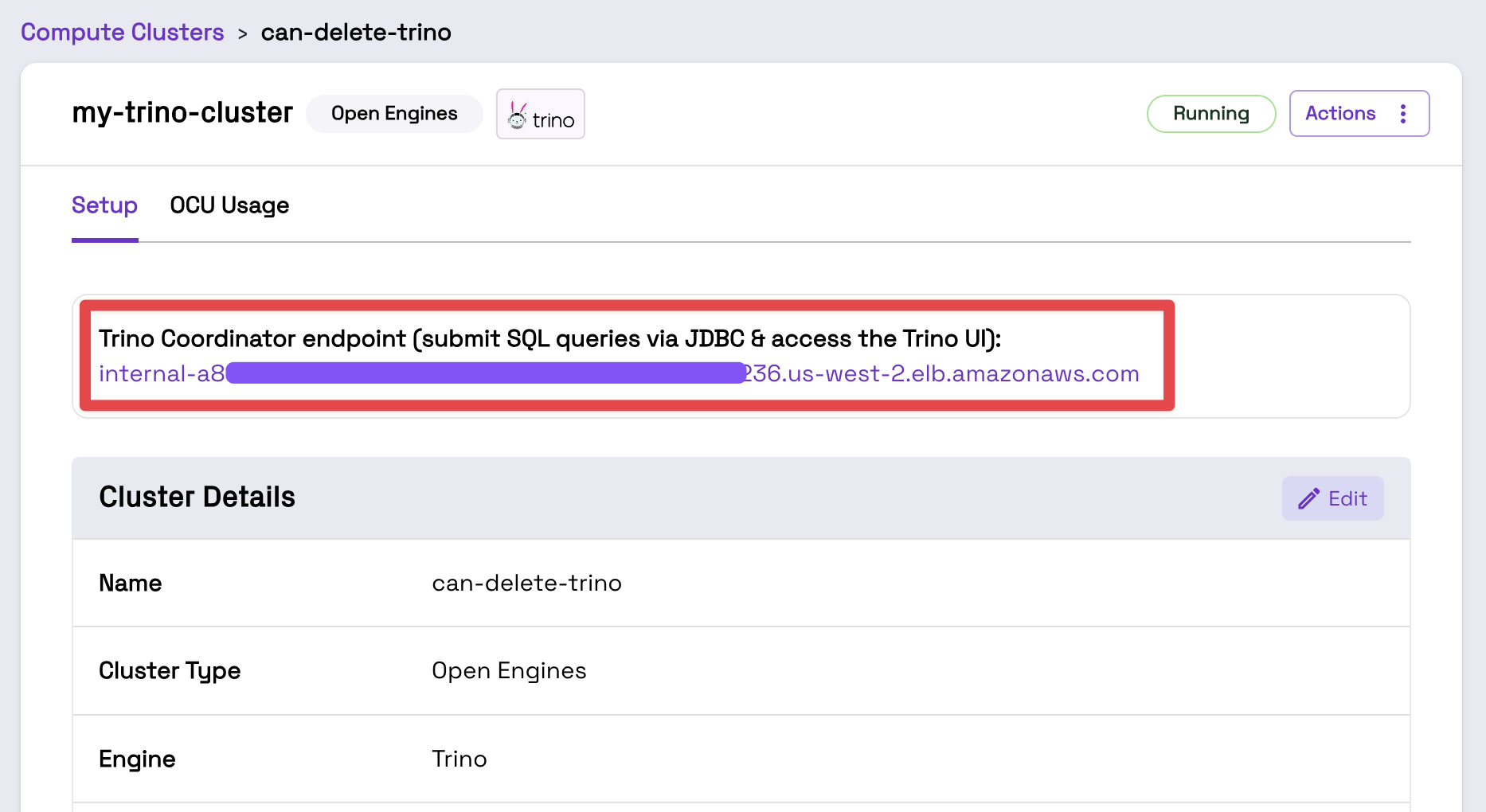
You will need to connect to the Cluster from within your VPC. To do this, you may use a VPN or SSH into a bastion host inside the VPC.
Next, open a SQL client, such as DBeaver. Create a Trino connection.
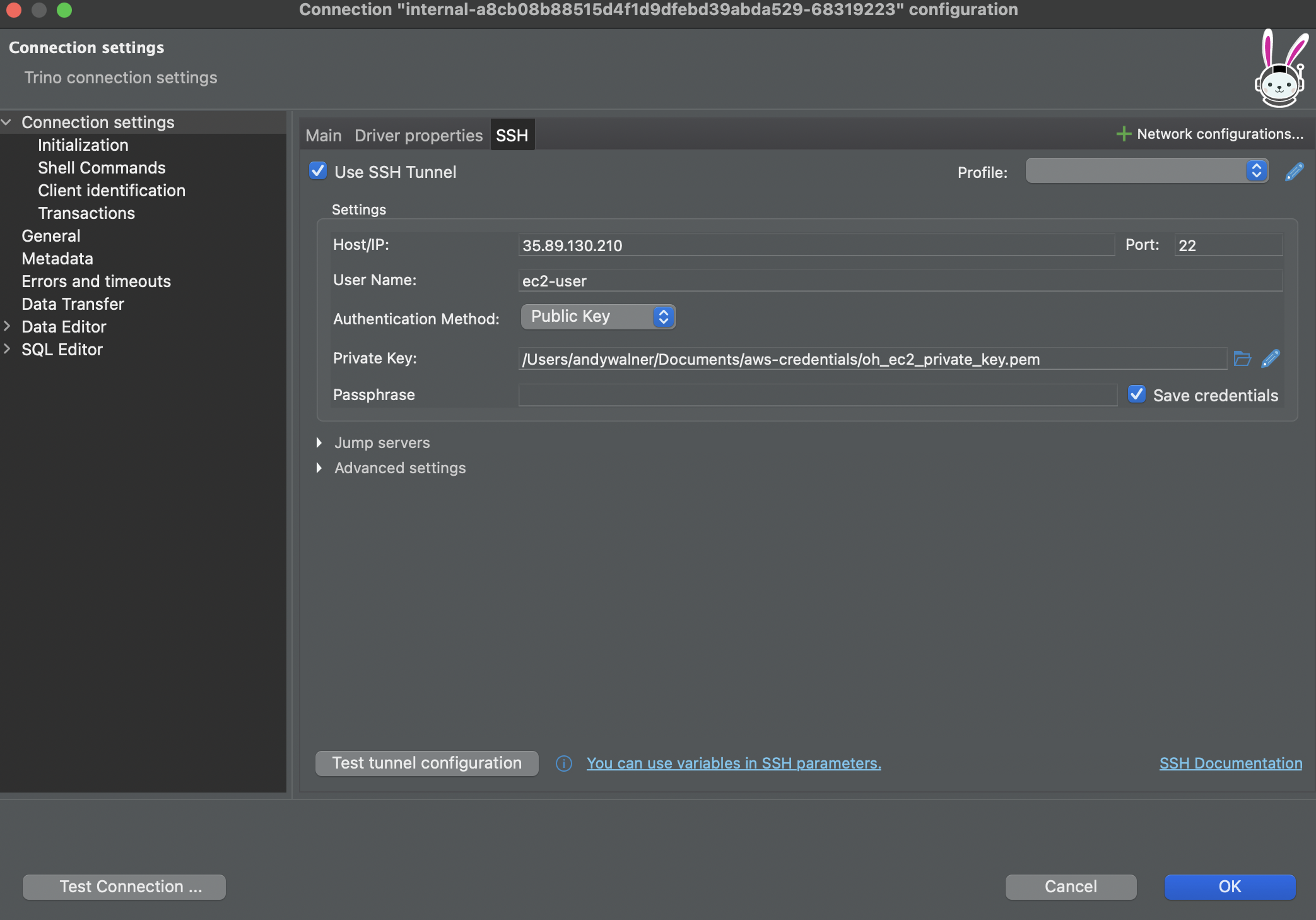
If you are connecting through SSH tunnel, add SSH credentials into the SQL client.
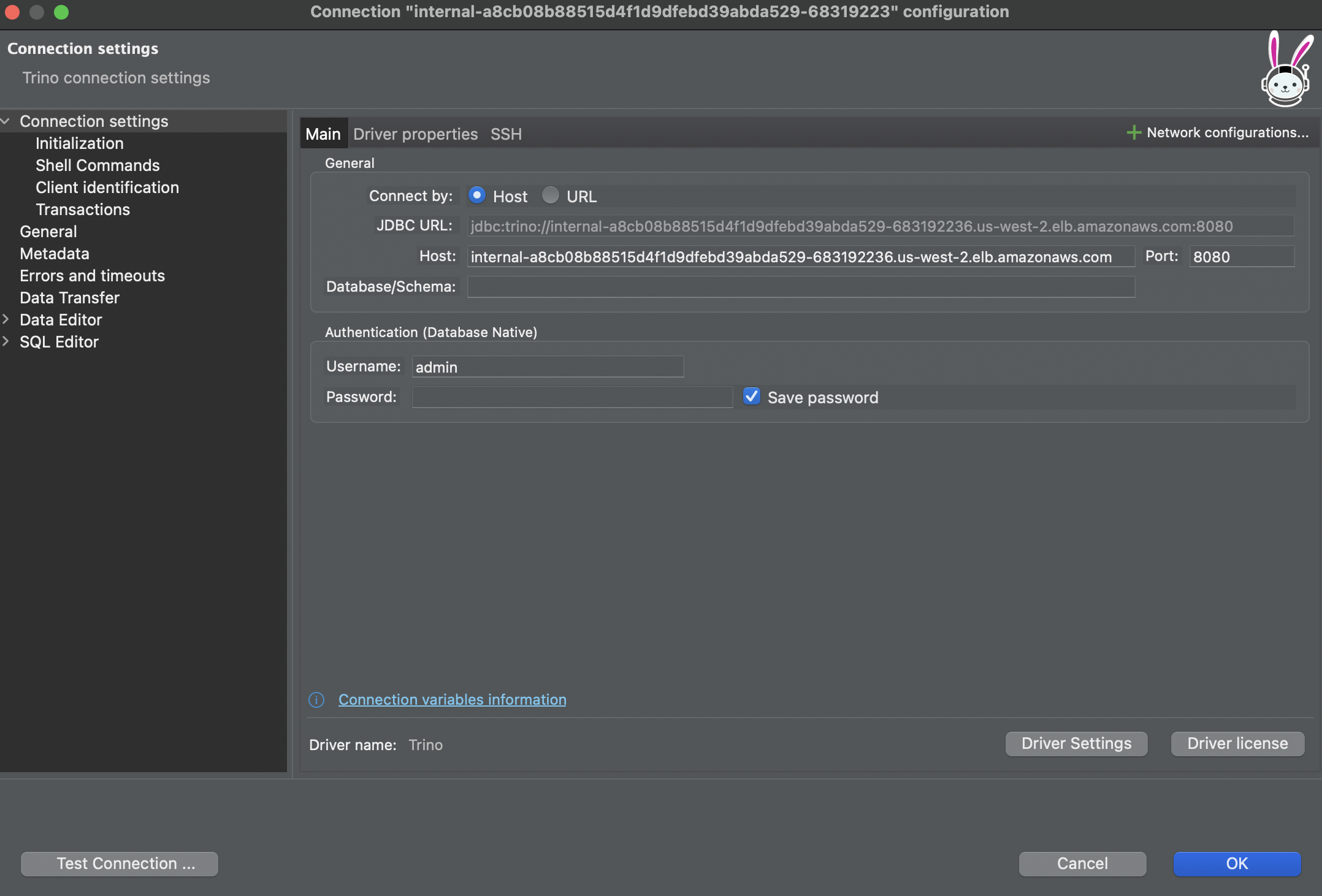
Finally, add your connection details. Paste the Trino coordinator endpoint url from the Onehouse console, and connect via port 8080. You may optionally specify a default database for the connection. For authentication, use admin as your username and leave the password empty.
After a successful connection, you will be able to view and query the tables from the catalog you configured for the Cluster.