Bronze to Silver ETL Pipeline with Python Job
Overview
This guide demonstrates how to implement a silver pipeline consuming from a bronze table created by Onehouse stream capture using Hudi and Onehouse Jobs.
The workflow transforms raw change data (users_pii) into a curated Silver table (users_from_jobs).
Use Case
We want to:
- Ingest change events from a raw table on-demand.
- Clean, deduplicate, and apply only the latest changes using a pre-combine key.
Pre-requisites
- Raw/Bronze table
users_piicreated by Onehouse stream capture - Create a cluster with "Cluster Type" as "Spark"
- Create
venv.tar.gzwith the required dependencies and upload it to S3. Follow the steps to create the file
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1: Create a etl_hudi.py file
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession, DataFrame
from typing import Optional
class LoggerProvider:
"""
Provides a Log4j logger that is prefixed with the fully qualified class name.
Useful for consistent and scoped logging across multiple modules/classes.
"""
def get_logger(self, spark: SparkSession, custom_prefix: Optional[str] = ""):
log4j_logger = spark._jvm.org.apache.log4j # noqa
return log4j_logger.LogManager.getLogger(custom_prefix + self._full_name_())
def _full_name_(self):
klass = self.__class__
module = klass.__module__
if module == "__builtin__":
return klass.__name__ # Avoid outputs like '__builtin__.str'
return module + "." + klass.__name__
class ProcessTable(LoggerProvider):
"""
Encapsulates operations to manage a Hudi table:
- Reads from an existing Hudi table using Spark SQL.
- Creates a new Hudi Merge-On-Read table using SQL.
- Writes a DataFrame to a Hudi table with record-key and precombine logic.
"""
def __init__(self, spark: SparkSession):
self.spark = spark
self.logger = self.get_logger(spark, "ReadFromTable")
def read_from_table(self, db_name: str, table_name: str):
"""
Reads all records from the given Hudi table using Spark SQL.
"""
self.logger.info(f"Reading from table: {db_name}.{table_name}")
df = spark.sql(f"SELECT * FROM {db_name}.{table_name}")
return df
def create_table(self, table_path: str):
"""
Creates the Silver Hudi table (`users_from_jobs`).
This table is defined with a primary key and pre-combine field for CDC support.
"""
sql = """
CREATE TABLE otcarp.users_from_jobs (
_change_operation_type STRING,
_upstream_event_processed_ts_ms BIGINT,
db_shard_source_partition STRING,
_event_origin_ts_ms BIGINT,
_event_tx_id BIGINT,
_event_lsn BIGINT,
_event_xmin BIGINT,
id INT,
name STRING,
ssn STRING,
email STRING,
signup_date TIMESTAMP
)
USING hudi
TBLPROPERTIES (
type = 'mor',
primaryKey = 'id',
precombineField = '_event_lsn'
)
LOCATION 's3a://lakehouse-albert-us-west-2/demolake/otcarp/users_from_jobs';
"""
self.logger.info(f"Creating table at {table_path}")
self.spark.sql(sql)
def write_to_table(self, df: DataFrame, table_name: str, table_path: str):
"""
Writes a DataFrame to a Hudi table using append mode with necessary options.
Uses 'id' as the record key and '_event_lsn' as the precombine field.
"""
hudi_options = {
'hoodie.table.name': table_name,
'hoodie.datasource.write.recordkey.field': 'id',
'hoodie.datasource.write.precombine.field': '_event_lsn'
}
df.write \
.format("hudi") \
.options(**hudi_options) \
.mode("append") \
.save(table_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize Spark session
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("ReadFromHudiTable").getOrCreate()
# Instantiate the processing class
process_table = ProcessTable(spark)
# Step 1: Create the Silver table if not exists
process_table.create_table("s3a://lakehouse-albert-us-west-2/demolake/otcarp/users_from_jobs")
# Step 2: Read CDC data from the raw/bronze Hudi table
hudi_df = process_table.read_from_table("otcarp", "users_pii")
# Step 3: Write data to the curated Silver Hudi table
process_table.write_to_table(
hudi_df,
"users_from_jobs",
"s3a://lakehouse-albert-us-west-2/demolake/otcarp/users_from_jobs"
)
Step 2: Upload the Python file to S3
Use AWS CLI or the AWS Console to upload the etl_hudi.py file to your S3 bucket.
Make sure to upload to the bucket which Onehouse has access to. If you are not sure, validate your terraform stack or CloudFormation stack.
Step 3: Create a Job in Onehouse
- Go to the Onehouse UI and navigate to the Jobs section.
- Click on "Create Job"
- Use an appropriate name i.e. "demo"
- Select the "Python" job type
- Select the "Spark" cluster
- Input the following in the "Parameters" section
["--conf", "spark.archives=s3a://lakehouse-albert-load-us-west-2/python/venv.tar.gz#environment", "--conf", "spark.pyspark.python=./environment/bin/python", "s3a://lakehouse-albert-load-us-west-2/python/read_hudi_table.py"]
Step 4: Run the Job
Once this job succeeds, your table will be available in the Onehouse Data Catalog.
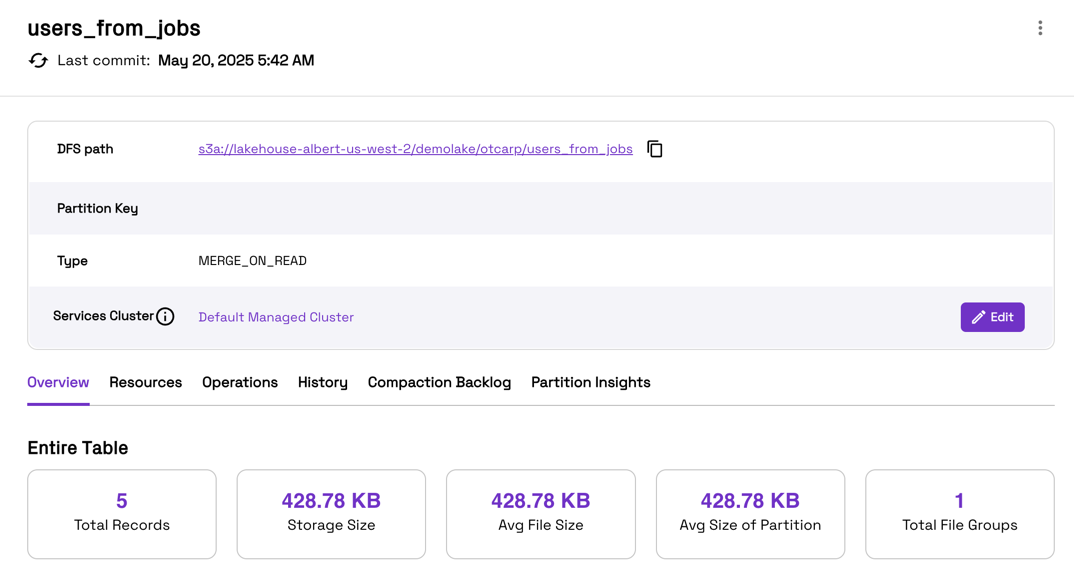
🏅 Step 4: Query the Silver Table
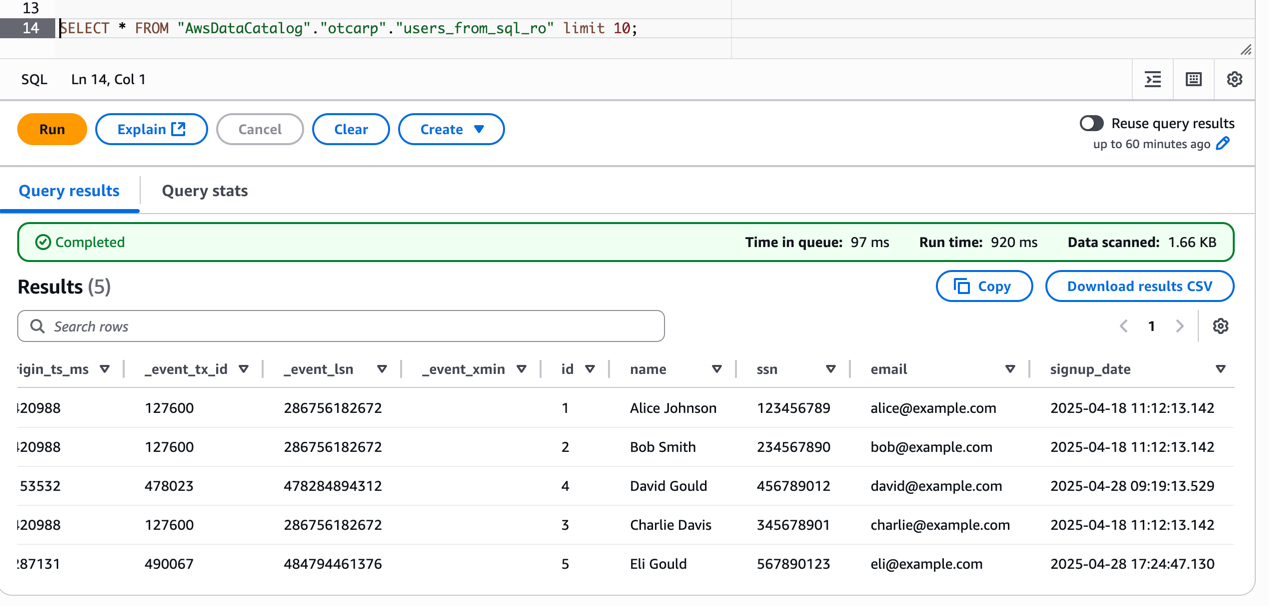
From external tools like Athena, you can query the Silver table using the following SQL:
SELECT * FROM "AwsDataCatalog"."otcarp"."users_from_sql_ro" limit 10;
Next Steps
If you want to automate this process, you can use an orchestration tools like Dagster and Airflow to schedule the Onehouse Job.